
The project scope is defined, key stakeholders are in agreement, you’re confident you can stay within the budget, and the project team is ready to dive in. Given that Low=$10k, Medium=$20K, High=$35K ProjectĬorrect Answer: B.Imagine you’re the assigned project manager on a high-stakes project. From the data given below, which project risk should be addressed first?.The decision tree is a diagram describing different decisions under consideration and the impact on the project of choosing one over the other.

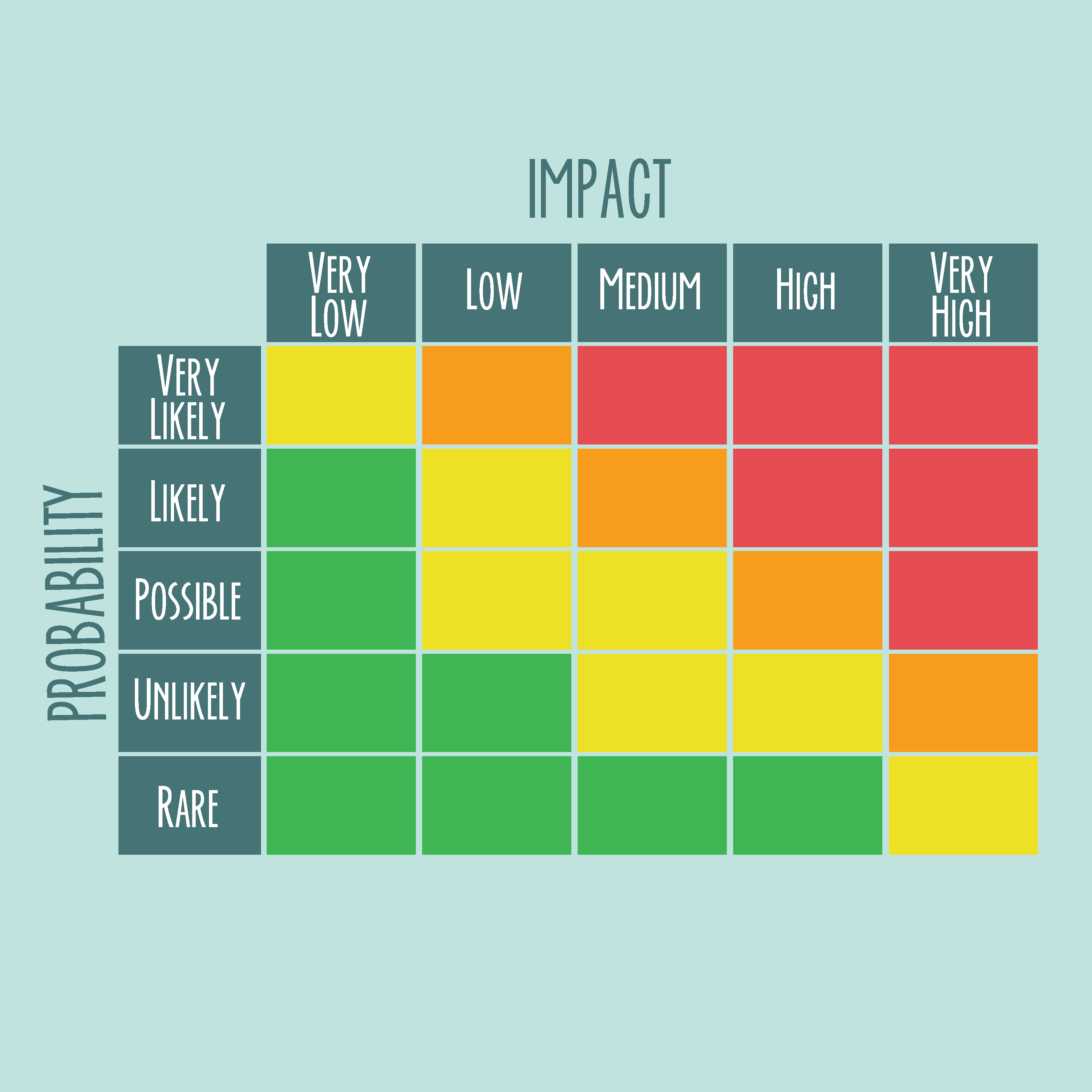
A probabilistic outcome prediction methodĬorrect Answer: B. Decision tree analysis can be classified as _? This matrix is typically defined by each organization internally. For example, a risk event with a high probability of occurring and a high impact will likely need a response plan.

The risk impact scale can be a relative scale (also known as an ordinal scale) that assigns values such as high-medium-low or a numeric scale known as a cardinal scale. Impact: Impact is the amount of pain (or the amount of gain) the risk event poses to the project.Probability is expressed as a number from 0.0-which means there is no probability of the event occurring-to 1.0-which means there is 100% certainty the risk will occur. The two responses added together equal 1.0. 50 chance of not getting heads on the flip. Note that the sum of probability that an event will occur and the probability that the event will not occur always equals 1.0. Probability: Probability is the likelihood that an event will occur.The tool and technique Risk probability and impact assessment calculate the probability that the risk events identified will occur, and it determines the effect their impacts have on the project objectives, including time, scope, quality, and cost. So with an expected value of $22,500 is the correct decision is to buy the new car. The decision of buying the New Car or Old car The square in this figure represent decision to be made, and the circles represent the points where risk events might occur. The expected monetary value of the decision is a result of the probability of the risk event multiplied by the impact for two or more potential outcomes and then summing their results. Figure below shows a sample decision tree with the Initial cost of buying the new car =$21,000 and that of buying the old car =$16000. Decision trees are usually used for risk events associated with time or cost. The available choices are depicted in tree form starting at the left with the risk decision branching out to the right with possible outcomes. Generally more than one choice or option is available when it comes to arriving to a decision or, in this case, potential outcomes from a risk event.
PMI RISK PROBABILITY IMPACT MATRIX HOW TO
This example shows how to calculate the total EMV Work Packageĭecision trees are diagrams that show the sequence of interrelated decisions and the expected results of choosing one alternative over the other. Positive results generally mean the risks occurring are opportunities to the project, while negative results generally indicate a threat to the project.ĮMV = P * I Where P is the Probability and I = Impact EMV is used in conjunction with the decision tree analysis technique, which is covered next. EMV is calculated by multiplying the probability of the risk by its impact for two or more potential outcomes (for example a good outcome and a poor outcome) and then adding the results of the potential outcomes together. Risk probability and impact calculationsĮxpected monetary value (EMV) analysis is a statistical technique that calculates the average, anticipated future impact of the decision.This article will cover the following tools and technique of Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis and Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis. Project Management Mathematics IV- Planning


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
